Headaches are a common complaint and often harmless, but certain types signal a serious health risk. One of these is the “thunderclap headache,” a sudden and severe headache that demands urgent medical care. If you or someone you know experiences this, don’t brush it off—it could be a sign of a life-threatening condition. Let’s delve into what makes a thunderclap headache so dangerous, its symptoms, and why immediate action is crucial.
What is a Thunderclap Headache?

A thunderclap headache gets its name from the sudden, explosive onset of pain that feels as if you’ve been struck on the head. Unlike typical headaches that might build gradually, a thunderclap headache reaches peak intensity within seconds, catching most people off-guard. This headache is often described as “the worst headache of your life,” and it isn’t something that fades with a glass of water or painkillers.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Thunderclap Headache
The symptoms of a thunderclap headache can vary, but its hallmark feature is the rapid onset of severe pain. This pain typically peaks within 60 seconds, causing overwhelming discomfort. Alongside intense head pain, other symptoms often include:
- Nausea and Vomiting: This intense headache can bring on queasiness, sometimes followed by vomiting.
- Fever: A high temperature may accompany the headache, signaling a possible infection or inflammation.
- Neck Pain and Stiffness: Pain can radiate to the neck and shoulders, making it difficult to move comfortably.
- Altered Mental State: Confusion, disorientation, or an inability to concentrate may occur.
- Seizures: In some cases, thunderclap headaches can induce seizures, adding to the urgency of seeking help.
These symptoms often feel like a bad headache, but they shouldn’t be ignored. Thunderclap headaches are unusual and require immediate medical assessment.
Why Thunderclap Headaches are Considered Dangerous
@drjoe_md Recognizing the symptoms of a spontaneous brain bleed, also known as a hemorrhagic stroke, is crucial for prompt medical attention. Key symptoms include a sudden and severe headache often described as the worst headache of one’s life, sudden confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg—especially on one side of the body—vision problems in one or both eyes, difficulty walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination, and a sudden severe headache. In severe cases, the individual may experience nausea, vomiting, seizures, or loss of consciousness. If any of these symptoms occur suddenly, immediate medical care is essential. #stroke #headache #neckpain #emergencymedicine ♬ original sound – Dr. Joe, M.D. 🩺
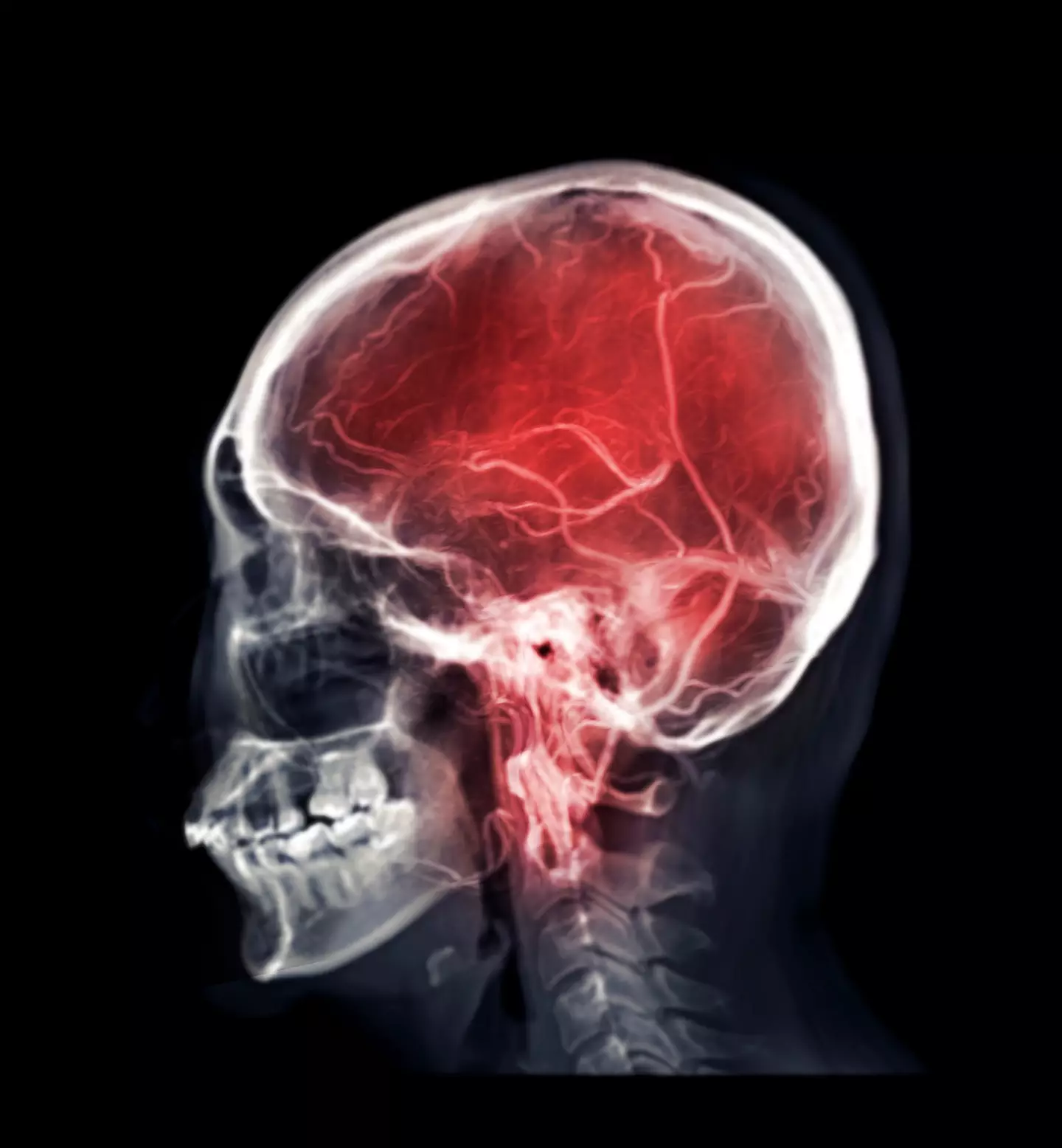
A thunderclap headache isn’t just painful—it’s potentially deadly. Often, this type of headache can be a sign of a burst brain aneurysm, a medical emergency that causes bleeding in the brain. The burst leads to what’s known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage, where blood fills the space between the brain and its protective covering. This hemorrhage can increase pressure on the brain, potentially leading to permanent brain damage or death if untreated.
While not every severe headache is a thunderclap headache, it’s vital to know the difference because of the high-risk factors associated with it. In many cases, ignoring a thunderclap headache can have dire consequences, so erring on the side of caution is the safest course.
Differentiating Thunderclap Headaches from Other Types of Headaches
Medical professionals classify headaches into types like tension, cluster, sinus, and migraine, each with unique characteristics. But thunderclap headaches stand out due to their sudden intensity. Here’s a quick comparison:

- Tension Headaches: These usually feel like a band tightening around your head, with a gradual onset.
- Migraine Headaches: Migraines may include throbbing pain, light sensitivity, and nausea but typically build up over time.
- Cluster Headaches: Known for intense pain around one eye, cluster headaches tend to come in “clusters” over weeks, unlike the one-off nature of thunderclap headaches.
- Thunderclap Headaches: With a thunderclap headache, pain appears out of nowhere, reaches maximum intensity almost instantly, and feels unlike any typical headache.
The suddenness and intensity of a thunderclap headache set it apart, marking it as a red flag for serious health conditions.
When to Seek Medical Help for a Thunderclap Headache
If you experience a thunderclap headache, it’s essential to go to the hospital immediately. Waiting it out or assuming it’s just a bad headache could delay necessary treatment, putting you at further risk. Here’s when you should absolutely seek medical attention:
- Sudden, Extreme Pain: If the headache is sudden and feels unlike any headache you’ve experienced before.
- Associated Symptoms: If you also have nausea, vomiting, seizures, fever, or any of the other symptoms previously mentioned.
- Loss of Consciousness or Seizures: Any fainting or seizure activity requires urgent medical attention.
Time is critical in these situations, as prompt intervention can make a significant difference in the outcome.
Causes of Thunderclap Headaches: What You Need to Know
Understanding the underlying causes of thunderclap headaches can shed light on why they’re so dangerous. Common medical reasons for these headaches include:
- Brain Aneurysm: A brain aneurysm is a bulging blood vessel in the brain. When it bursts, it causes a thunderclap headache, often leading to a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: This rare condition involves blood clots in the brain’s veins, causing intense pain and other neurological symptoms.
- Stroke or Hemorrhage: Strokes, particularly hemorrhagic strokes, can present with sudden, severe headache pain.
- Infections like Meningitis: Meningitis and encephalitis (brain inflammation) can also present as severe headaches with accompanying fever and neck stiffness.
These causes range from blood vessel issues to infections, each of which requires specialized medical treatment. Identifying the cause early is essential, as it influences the treatment approach and prognosis.
How Thunderclap Headaches are Diagnosed and Treated
If you experience a thunderclap headache and go to the hospital, the diagnostic process is thorough. Doctors may conduct the following tests:

- CT Scan: A CT scan of the head quickly identifies bleeding in the brain, which is common in subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): This test checks for blood or infection in cerebrospinal fluid, helping to rule out or confirm specific diagnoses like meningitis.
- MRI or Angiography: These imaging tests can reveal problems with blood vessels or areas of inflammation in the brain.
Treatment will vary depending on the underlying cause. For instance, if a burst aneurysm is identified, surgery or other procedures may be necessary to repair the vessel and prevent further bleeding.
Why Early Intervention Matters
Quick action is the best defense against the dangerous outcomes associated with thunderclap headaches. Recognizing the signs and getting to a hospital quickly gives you the best chance of successful treatment and recovery. In cases of aneurysms or hemorrhages, early intervention can prevent permanent brain damage and even save lives.
Conclusion
Thunderclap headaches are a medical emergency, and they’re not to be ignored or downplayed. Recognizing the symptoms—sudden, intense pain accompanied by nausea, confusion, or seizures—could be lifesaving. Understanding these warning signs and acting promptly could mean the difference between recovery and a more tragic outcome. So, if you or someone around you experiences the worst headache of their life, take it seriously and seek medical help immediately.